Let's Understand Biometrics
- 26 Oct, 2023
- Tech
- 587 Views
- 0 Comments
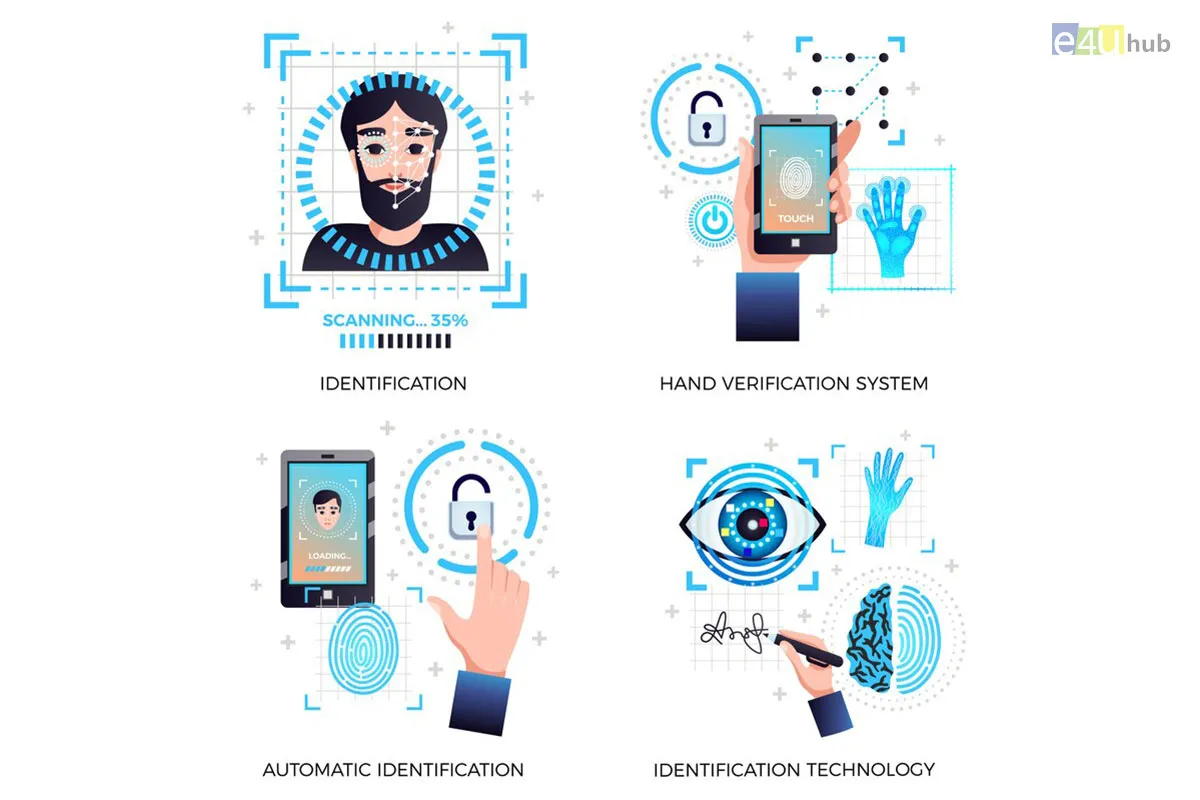
Biometrics refers to the measurement and statistical analysis of people's unique physical and behavioral characteristics. These characteristics are used to verify their identity or to grant them access to specific systems, devices, or locations. Biometric authentication systems have become increasingly popular because they provide a secure and convenient way to identify and authenticate individuals. Here are the key aspects of biometrics:
Types of Biometric Characteristics:
1. Fingerprint Recognition: This is one of the oldest and most widely used biometric methods. It involves scanning the unique patterns found in an individual's fingerprints.
2. Facial Recognition: This technology uses facial features, such as the distance between eyes, nose, and mouth, to identify individuals. It's often used in security systems and smartphones.
3. Iris Recognition: Iris recognition scans the unique patterns in the colored part of the eye (iris) to verify a person's identity. Iris patterns are highly unique and do not change over time.
4. Voice Recognition: Voice biometrics analyzes a person's unique vocal patterns and characteristics. It's used in various applications like phone banking and voice assistants.
5. Palmprint Recognition: Similar to fingerprints, palmprints are unique to individuals. Palmprint recognition systems use the patterns and ridges on a person's palm to identify them.
6. Behavioral Biometrics: This includes the study of typing patterns, gait analysis, and other behavioral patterns. It focuses on the unique way individuals perform tasks.
How Biometric Systems Work:
1. Enrollment: During enrollment, an individual's biometric data is captured and stored securely in a database. For example, in fingerprint recognition, the unique fingerprint patterns are recorded.
2. Comparison: When authentication is required, the biometric system compares the captured biometric data with the stored data. Various algorithms are used to match the patterns.
3. Decision: Based on the comparison, the system makes a decision. Access is granted if the captured data matches the stored data within a certain threshold. Otherwise, it's denied.
Advantages of Biometrics:
1. Security: Biometrics offer a high level of security because they are unique to individuals and difficult to forge.
2. Convenience: Biometric authentication is convenient as it doesn't require memorizing passwords or carrying access cards.
3. Accuracy: Biometric systems, when properly calibrated, can be highly accurate in identifying individuals.
Challenges and Concerns:
1. Privacy: Storing and sharing biometric data raises privacy concerns. People worry about how their biometric data is being used and protected.
2. Security Risks: Biometric data, once compromised, cannot be changed. If someone gains unauthorized access to biometric databases, it could lead to identity theft.
3. Cultural and Social Acceptance: In some cultures, the use of biometrics is a sensitive topic, and there are concerns about its social acceptance and implications.
In summary, biometrics offer a powerful means of authentication and identification, but careful consideration of privacy, security, and ethical concerns is crucial in their implementation and use.














Leave a Reply